|
Chemicals
 Propionic anhydride
Propionic anhydride
Propionic anhydride
CAS number 123-62-6
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
 CAS
NO. 123-62-6 CAS
NO. 123-62-6
PROPIONIC ANHYDRIDE EINECS NO. 204-638-2
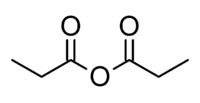
FORMULA C2H5COOCOC2H5
MOL WT. 130.14
H.S. CODE 2915.90
TOXICITY Oral rat LD50: 2360 mg/kg
SYNONYMS methylacetic anhydride; Propionyl oxide;
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
PHYSICAL STATE clear liquid
MELTING POINT -45 C
BOILING POINT 167 C
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.01
SOLUBILITY IN WATER Insoluble (decomposes slowly) pH
VAPOR DENSITY 4.5
AUTOIGNITION 285 C
NFPA RATINGS Health: 3 Flammability: 2 Reactivity: 1
REFRACTIVE INDEX 1.403 - 1.405
FLASH POINT 63 C
STABILITY Stable under ordinary conditions
Propionic anhydride is chiefly used as a raw material for
cellulose acetate propionate, a plaxtic found in face shields,
sunglasses, brush handles, toys, cosmetics containers and blister
packages. Propionic anhydride is also a raw material for dyes,
pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and fragrance chemicals.
Physical data
Appearance: colourless liquid with an unpleasant odour
Melting point: -45 C
Boiling point: 167 C
Vapour density: 4.5 (air = 1)
Vapour pressure:
Density (g cm-3): 1.01
Flash point: 63 C
Explosion limits: 1.3 - 9.5%
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility: decomposes
Stability
Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents,
water, moisture, most common metals, active halogen compounds,
ammonia, amines.
Personal protection
Safety glasses, good ventilation.
Hazards
Air & Water Reactions
Decomposes exothermically in water to form a corrosive solution of
propionic acid [Merck, 11th ed. 1989].
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily.
Substance will react with water (some violently) releasing
flammable, toxic or corrosive gases and runoff. When heated, vapors
may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers
explosion hazards. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will
spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers,
basements, tanks). Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash
back. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas.
Containers may explode when heated or if contaminated with water.
(ERG, 2008)
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes irritation of eyes and respiratory tract. Contact
with liquid causes burns of eyes and skin. Ingestion causes burns of
mouth and stomach. (USCG, 1999)
Reactivity Profile
PROPIONIC ANHYDRIDE reacts exothermically with water. The reactions
are sometimes slow, but can become violent when local heating
accelerates their rate. Acids accelerate the reaction with water.
Incompatible with acids, strong oxidizing agents, alcohols, amines,
and bases.
STORAGE
Separated from acids, bases, oxidants, food and feedstuffs. Dry.
Ventilation along the floor.
DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
Propionic anhydride is a clear liquid with an unpleasant odour. It
hydrates with water producing corrosive propionic acid. It is
miscible in most organic solvents and decomposes with alcohol.
Propionic anhydride used as an intermediate to produce dyes,
pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals and other organic compounds.
SALES SPECIFICATION
APPEARANCE
clear liquid
CONTENT 98.0% min
PROPIONIC ACID 2.0% max
OTHER INDIVIDUAL IMPURITY 0.5% max
COLOR 20 max (Pt/Co scale)
Safety
Propanoic anhydride is strong smelling and corrosive, and will cause
burns on contact with skin. Vapour can burn eyes and lungs.
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 |



